How Does Chronic Stress Affect Your Body?

What is Stress?
When we think of stress, we typically think of external factors like jobs, hectic schedules, and national and international emergencies.
But stress is designed to help your body react to dangerous situations.
When you perceive a threat, your body is triggered to release several stress hormones, including cortisol and adrenaline.
These hormones help keep you alert and aware of your surroundings, and to quickly escape danger if needed.
The Problem with Ongoing Stress
The problem starts when we experience emotional and psychological stressors over long periods of time without any relief. In these situations, the stressor is much more complex, and it’s not easily solved. Some chronic stress examples include pressure to perform at work, or conflict in a marriage or close personal relationship.
Because we can’t solve these stressors immediately, we experience prolonged stress responses with no break.
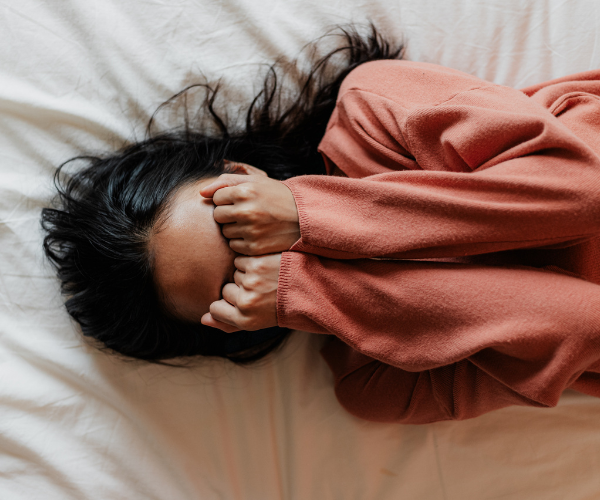
This is chronic stress, and it can have a damaging impact on physical and mental health, the endocrine system, the immune system, and others.
Here’s an overview of what chronic stress can do to your body, and some tactics you can use to minimize the effects of stress.
Chronic Stress Symptoms
Chronic stress symptoms can vary from person to person, but some of its effects can include:
- Irritability and changes in mood
- Anxiety or nervousness
- Loss of concentration
- Fatigue
- Difficulty sleeping
- Low sex drive
- Rapid, spiraling thoughts
- Weight gain, especially fat gain
- A decreased immune system and frequent illness
- Joint pain
- High blood pressure
Chronic stress symptoms can affect many systems throughout the body, including the endocrine and immune systems. It can also influence weight gain, cardiovascular health, and more.
How to Treat Chronic Stress
Stress is unavoidable, and everyone will experience it at some point. But if you have high levels of chronic stress, you can try these strategies to help mitigate its harmful effects.
1. Figure out what’s causing your stress.
To start addressing chronic stress, you first have to figure out where’s it’s coming from. Some common chronic stress examples are work pressures, balancing family obligations, financial instability, and disasters that are out of our control.
To find out your biggest stressors, try writing down every time you experience a spike of stress throughout the day, and then look over your notes for patterns. Once you have an idea of what triggers your stress, you can build strategies to help minimize or mitigate the effects of those stressors.
2. Prioritize sleep.
Sleep is extremely important to overall health and wellbeing. Lack of sleep can make you more likely to experience medical conditions like diabetes and heart disease, and it can even shorten life expectancy.
Because prolonged stress often causes difficulty sleeping, it’s important to prioritize your sleep schedule.
To improve your sleep, try these strategies:
- Set a regular sleep schedule and stick to it. Go to bed at the same time each night and wake up at the same time – even on weekends.
- Take time to relax before bed. If you’re having trouble going to sleep, it may be because you’re keeping your brain active until the moment you lay down. Commit to putting down your phone, turning off the television, and doing a relaxing activity like reading or meditation before bed. Avoid looking at any kind of screen for at least an hour before bed, since the light from the screen can keep your brain awake.
- Keep your bedroom free of stressors. Don’t leave a stack of bills on the dresser or your work laptop on the nightstand. Try to make your bedroom environment as relaxing as possible, so your stress isn’t triggered while trying to sleep.
- If you experience insomnia, don’t just toss and turn in bed. Get up and perform a low-stress and repetitive activity, like folding laundry, in dim light. This can help you relax your brain, and it can also help you avoid feeling anxious and upset while in bed.
3. Set boundaries.
While you can’t always control the stressors in your life, you can set boundaries to mitigate the stress they cause. An example is to avoid answering work emails after 9 PM, or create a To-Do list and allow yourself to stop after you’ve finished it – without adding anything new.
Most of us have jobs and lives that never stop. There’s always something we could be doing, and sometimes the pressure to be productive exacerbates chronic stress. Evaluate what you can get done in a day, and then set boundaries around that.
4. Find effective supplements and medications.
Changing your behaviors and habits can help manage prolonged stress. But you can also get assistance through nutritional supplementation and medications. See our list of top 12 supplements and medications that can help you balance your stress levels.
Vitamins and nutritional supplements
B vitamins – like B12, B3, B5 and B6 – can help boost your mood and offset chronic stress symptoms. Other supplements, like hydroxytryptophan (HTP-5), can help regulate the level of serotonin in the central nervous system and brain, which can assist with depression and other symptoms related to chronic stress.
Melatonin can act as a natural sleep aid to help you get the sleep you need. Magnesium plays an important role in sleep and in overall health, and it can be a useful supplement for those with chronic stress.
Hormone Replacement Therapy
When you balance your hormones and bring them up to optimal ranges, you can experience many positive changes throughout your body. Our patients report feeling better, having more energy, losing excess fat, and being healthier overall.
Hormones that can help with stress and overall health and wellbeing are testosterone, estrogen (for women), pregnenolone, and DHEA (dehydroepiandrosterone), among others.

Stress Management with Defy Medical
Now you have a basis of understanding about chronic stress, chronic stress symptoms, and some strategies you can adopt to combat ongoing stress in your life.
If you’re interested in hormone replacement therapy and supplementation to help manage chronic stress, you can contact Defy Medical today to learn more about becoming a patient.
Get Started